边界网关协议(英语:Border Gateway Protocol,缩写:BGP)是互联网上一个核心的去中心化自治路由协议。它通过维护IP路由表或“前缀”表来实现自治系统(AS)之间的可达性,属于矢量路由协议。BGP不使用传统的内部网关协议(IGP)的指标,而使用基于路径、网络策略或规则集来决定路由。因此,它更适合被称为矢量性协议,而不是路由协议。
大多数互联网服务提供商必须使用BGP来与其他ISP创建路由连接(尤其是当它们采取多宿主连接时)。因此,即使大多数互联网用户不直接使用它,但是与7号信令系统——即通过PSTN的跨供应商核心响应设置协议相比,BGP仍然是互联网最重要的协议之一。特大型的私有IP网络也可以使用BGP。例如,当需要将若干个大型的OSPF(开放最短路径优先)网络进行合并,而OSPF本身又无法提供这种可扩展性时。使用BGP的另一个原因是其能为多宿主的单个或多个ISP网络提供更好的冗余。
AS就是一个独立管理的网络。大公司或者组织的网络一般是由一到多个AS组成,小的公司或者个人是通常会接入到ISP(Internet Service Provider)的AS。不管怎么样,如果设备在互联网上,那么必定是属于某一个AS。EBGP是用来连接各个AS,这样互联网上的设备的才能够彼此互连。AS之间的连接协议,目前在用的,有且仅有EBGP一种。
在bgp网络中,具有相同AS号的peer称为IBGP(internal peer),而具有不同AS号的peer称为EBGP(external peer)。IBGP应用在AS内部,作为IGP的一种。一般的IGP,例如OSPF,EIGRP,用来在邻接路由器之间传递路由。而IBGP可以用来在edge router之间同步路由,edge router并不需要邻接。Edge router是指在AS边缘,用来连接其他AS的router,那么edge router肯定是运行了EBGP。同时这个edge router也会有对端AS的路由。通过IBGP,edge router会将学习到的对端AS的路由,传递给其他的edge router。这样,可以实现跨AS的连通。
bgp使用使用tcp 179端口就行通信,消息格式按照TLV形式构成,其中T是消息类型,L是消息长度,V是具体的消息。bgp-4(针对ipv4路由,参考rfc2858查看ipv6和其他协议路由)中一共定义了4个核心消息类型,分别为OPEN,UPDATE,KEEPALIVE,NOTIFICATION。其中OPEN用来在建立peer链接时使用,此处还有一个扩展协议rfc2842定义了基于OPEN消息的扩展属性,给双方提供的协商自身能力的能力;UPDATE用来更新和撤销路由信息,KEEPALIVE用来维护peer链接的心跳,NOTIFICATION用来在出错时进行通知,在rfc2918中还定义了一个ROUTE-REFRESH类型的消息,用来实现路由的全量刷新。
UPDATE用来在peer之间进行路由的更新和撤销操作,其中最重要的是UPDATE消息,其消息的格式参考如下:
UPDATE消息用来向peer端公布(advertise)可行的具有相同路径属性的路由,或者撤销不再
可行的路由。单条UPDATE消息既可以公布路由,也可撤销之前公布的路由。
+-----------------------------------------------------+
| 撤销的路由信息长度(2字节) |
+-----------------------------------------------------+
| 撤销的路由信息(变长) |
+-----------------------------------------------------+
| 路径属性信息长度(2字节) |
+-----------------------------------------------------+
| 路径属性(变长) |
+-----------------------------------------------------+
| 网络层可达性信息(NLRI)(变长) |
+-----------------------------------------------------+
撤销的路由信息长度:
两字节无符号整形,标识撤销的路由信息的数据总长度。通过该值可以定位到NLRI
在数据流中的位置。
0值意味着没有路由信息被撤销,那么撤销的路由信息不包含在这条消息中。
撤销的路由信息:
可变长度的字段,包含了正在被撤回的IP地址前缀列表。每个IP地址前缀使用二元组
<长度,前缀>表示,含义如下:
+---------------------------+
| 长度(1字节) |
+---------------------------+
| 前缀(变长) |
+---------------------------+
这两个字段的含义如下:
a) 长度:
表示IP地址前缀的bit位是多少,0值表示匹配所有IP地址。
b) 前缀:
IP地址前缀,后面跟随着一些bit位用来进行字节对其,这些用来补齐的bit没有
实际用途,值无所谓。
路径属性信息长度:
这是一个两字节编码的无符号证书表示路径属性信息的数据总长度,通过该值可以定位
到网络可达性信息在数据流中的位置。
0值表示该UPDATE消息中没有路径属性信息和网络可达性信。
路径属性
在每条UPDATE消息中都包含路径属性信息,除非是一条只有撤销信息的消息。每一条路径
属性信息都由这样可变长度的三元组组成:<属性类型,属性长度,属性值>。
属性类型占2字节,包含属性标志位字节和属性类型字节。
0 1
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| Attr. Flags |Attr. Type Code|
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
属性标志位中的高位的bit(bit 0)是可选标志,表示该属性是否为可选的,如果为1则
是可选的属性,为0则是强制的(广为人知的)。
属性标志位中的第二高位的bit(bit 1)是传递标志,表示可选属性是否可被传递,为1
则表示可传递,为0则表示不可传递。
对于广为人知的属性,传递位的值必须设置为1.
属性标志位中的第三高位的bit(bit 2)是部分标志,表示可选的可传递的属性是否是
一部分(1)还是完整的(0)。对于广为人知的属性,和可选的不可传递属性,该为必须
设置为0。
属性标志位中的第四高位的bit(bit 3)是扩展长度标志,表示该属性的长度是用一个
字节表示(0)还是用两个字节表示(1)。
属性标志位中的低位的四个字节是未使用的,必须设置为0,并且接收端要忽略。
属性类型代码字节包含了属性的类型代码号,当前已经定义了的代码号参考第五部分。
如果扩展长度标志位为1则第三位和第四位表示值的长度,如果为0则第三位表述值的长度
剩下的字节都是该属性的值,需要根据属性的标志和属性代码做具体的解释。当前支持的
属性代码和属性值如下:
a) ORIGIN (Type Code 1):
ORIGIN是一个广为人知的强制属性,定义了该路径的来源是哪里。数据值的含义如下:
Value Meaning
0 IGP - Network Layer Reachability Information
is interior to the originating AS
网络可达性信息是来自于源AS内部。
1 EGP - Network Layer Reachability Information
learned via the EGP protocol [RFC904]
网络可达性信息是通过EGP学习到的。
2 INCOMPLETE - Network Layer Reachability
Information learned by some other means
网络可达性信息是通过其他方式学习到的。
Usage of this attribute is defined in 5.1.1.
b) AS_PATH (Type Code 2):
AS_PATH是一个广为人知的强制属性,由AS路径段构成的一个序列,每个AS路径段
由一个三元组组成<路径段类型,路径段长度,路径段值>
路径段类型占一个字节,含义如下
Value Segment Type
1 AS_SET: unordered set of ASes a route in the
UPDATE message has traversed
该路由经过的AS的无序集合。
2 AS_SEQUENCE: ordered set of ASes a route in
the UPDATE message has traversed
该路由经过的AS的有序集合。
路径段长度占一个字节,表示集合内数据的元素的程度。
路径段长度包含了一个或更多的AS编号,每个编号用2字节表示。
c) NEXT_HOP (Type Code 3):
下一跳是一个广为人知的属性,表示NLRI中的目的地的下一跳地址是这个,路由器在
对NLRI中的目的的数据包进行路由时应该发到这个IP上。
d) MULTI_EXIT_DISC (Type Code 4):
这是一个可选的不可传递属性,是一个四字节的无符号整数。该值可由BGP speeker
的决策进程来区别邻居自治域的不同入口。
e) LOCAL_PREF (Type Code 5):
这是一个广为人知的可选属性,是一个四字节的无符号整数。BPG speeker用该值
通知别的内部peer关于本speeker对该路由的偏好程度。
f) ATOMIC_AGGREGATE (Type Code 6)
ATOMIC_AGGREGATE is a well-known discretionary attribute of
length 0.
g) AGGREGATOR (Type Code 7)
这是一个可选的可传递属性,具有6字节的长度。表示最后一个AS号,生成了这个聚合
的路由信息(2字节),后面是这个speeker的IP地址(4字节),这个IP地址应该和
BGP peer链接中的标识IP相同。
网络可达性信息:
该可变长度字段包含了IP地址前缀组成的一个列表,该部分的数据长度没有明确的字段
表示,但是可以通过下面方式计算
UPDATE消息的总长度 - 23 - 总路径属性长度 - 撤销的路由信息的长度。
可达性信息使用一个或多个二元组<长度,前缀>编码表示,字段含义如下:
Reachability information is encoded as one or more 2-tuples of
the form <length, prefix>, whose fields are described below:
+---------------------------+
| Length (1 octet) |
+---------------------------+
| Prefix (variable) |
+---------------------------+
a) 长度:
IP地址前缀的位长度,0值表示匹配所有IP地址。
b) 前缀:
表示IP地址前缀,后面跟随一些补齐使用的bit位。
UPDATE消息的最小长度为23字节,19个消息头 + 2字节撤销路由长度 + 2字节路径属性。
UPDATE消息一次只可以公布一个路径属性的集合,但是可以包含多个目标地址,所有目标地址
都共享这些路径属性信息,这些路径属性信息应用于所有的RLRI。
UPDATE消息可以撤回多个路由信息,每条路由信息用IP地址前缀表示,明确的撤销之前本
bgp speeker和对端BGP speeker公布过的路由。当向BGP peer公布路由是,对于NEXT_HOP字段根据peer是IBGP还是EBGP会有不同的处理:
NEXT_HOP是一个广为人知的强制属性,为本条消息中列出的目的地指定下一跳路由器的IP地址,NEXT_HOP属性
的计算方法如下所示:
1) When sending a message to an internal peer, if the route is not
locally originated, the BGP speaker SHOULD NOT modify the
NEXT_HOP attribute unless it has been explicitly configured to
announce its own IP address as the NEXT_HOP. When announcing a
locally-originated route to an internal peer, the BGP speaker
SHOULD use the interface address of the router through which
the announced network is reachable for the speaker as the
NEXT_HOP. If the route is directly connected to the speaker,
or if the interface address of the router through which the
announced network is reachable for the speaker is the internal
peer's address, then the BGP speaker SHOULD use its own IP
address for the NEXT_HOP attribute (the address of the
interface that is used to reach the peer).
2) When sending a message to an external peer, X, and the peer is
one IP hop away from the speaker:
- If the route being announced was learned from an internal
peer or is locally originated, the BGP speaker can use an
interface address of the internal peer router (or the
internal router) through which the announced network is
reachable for the speaker for the NEXT_HOP attribute,
provided that peer X shares a common subnet with this
address. This is a form of "third party" NEXT_HOP attribute.
- Otherwise, if the route being announced was learned from an
external peer, the speaker can use an IP address of any
adjacent router (known from the received NEXT_HOP attribute)
that the speaker itself uses for local route calculation in
the NEXT_HOP attribute, provided that peer X shares a common
subnet with this address. This is a second form of "third
party" NEXT_HOP attribute.
- Otherwise, if the external peer to which the route is being
advertised shares a common subnet with one of the interfaces
of the announcing BGP speaker, the speaker MAY use the IP
address associated with such an interface in the NEXT_HOP
attribute. This is known as a "first party" NEXT_HOP
attribute.
- By default (if none of the above conditions apply), the BGP
speaker SHOULD use the IP address of the interface that the
speaker uses to establish the BGP connection to peer X in the
NEXT_HOP attribute.
3) When sending a message to an external peer X, and the peer is
multiple IP hops away from the speaker (aka "multihop EBGP"):
- The speaker MAY be configured to propagate the NEXT_HOP
attribute. In this case, when advertising a route that the
speaker learned from one of its peers, the NEXT_HOP attribute
of the advertised route is exactly the same as the NEXT_HOP
attribute of the learned route (the speaker does not modify
the NEXT_HOP attribute).
- By default, the BGP speaker SHOULD use the IP address of the
interface that the speaker uses in the NEXT_HOP attribute to
establish the BGP connection to peer X.
Normally, the NEXT_HOP attribute is chosen such that the shortest
available path will be taken. A BGP speaker MUST be able to support
the disabling advertisement of third party NEXT_HOP attributes in
order to handle imperfectly bridged media.
A route originated by a BGP speaker SHALL NOT be advertised to a peer
using an address of that peer as NEXT_HOP. A BGP speaker SHALL NOT
install a route with itself as the next hop.
The NEXT_HOP attribute is used by the BGP speaker to determine the
actual outbound interface and immediate next-hop address that SHOULD
be used to forward transit packets to the associated destinations.
The immediate next-hop address is determined by performing a
recursive route lookup operation for the IP address in the NEXT_HOP
attribute, using the contents of the Routing Table, selecting one
entry if multiple entries of equal cost exist. The Routing Table
entry that resolves the IP address in the NEXT_HOP attribute will
always specify the outbound interface. If the entry specifies an
attached subnet, but does not specify a next-hop address, then the
address in the NEXT_HOP attribute SHOULD be used as the immediate
next-hop address. If the entry also specifies the next-hop address,
this address SHOULD be used as the immediate next-hop address for
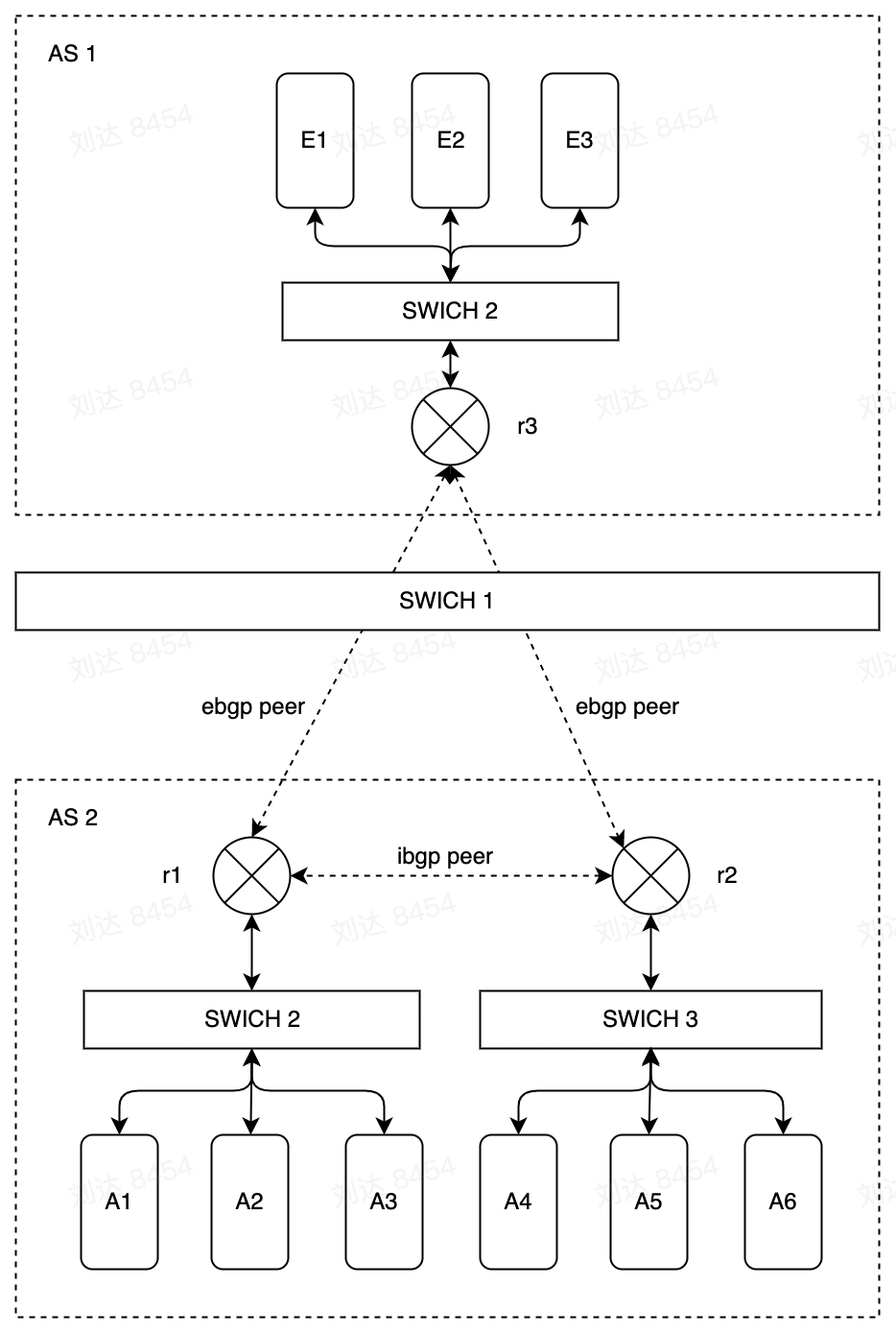
packet forwarding.在下图中,AS1和AS2是两个不同的自治系统。r1,r2和r3在两个自治系统中作为边界路由器。AS2中的r1,r2与AS1中的r3通过ebgp协议交换路由信息同步两个系统的路由信息。而AS2中的r1和r2通过ibgp协议同步交换该自治系统中的内部路由信息。
在kubernetes集群中,集群内各个节点都是bgp peer(上图中的router),运行bgp软件,通过协议将本机上pod的路由信息传递给其他节点上的peer端,其他节点会计算并配置改节点上的路由规则。集群内的每个节点之间可以互相建立peer连接,组成mesh。也可以使用其中数个节点作为reflector,其他所有节点连接到relfector,减少大规模集群中peer链接数量,reflector会将其他节点同步给自己的路由信息分发到其他节点上。